CodeSpitz78 1/ 루틴과 결합도-응집도 모델

🌕🌑🌑
🔥 코드스피츠 수업을 수강하면서 복습한 내용을 정리했습니다. 공부 후에는 풀어서 쉬운 언어로 설명할 수 있도록 연습하자.
1. Sub Routine
1-1. sub routine flow ### flow - 메모리에 적재되어있는 명령이 순차적으로 실행되는 과정을
의미한다. - sync라고도 한다.
routine
- 메모리에 적재되어있는 명령어 세트
- 명령어 세트를 한번만 부를 수 있으면 routine이라고 하지 않는다.
- 여러번 실행할수 있는 방법이 갖춰졌으면 루틴.
sub rotine
- main routine과 상대되는 개념
- 절대적인 개념이 아니다.
- 자식클래스 <-> 부모클래스
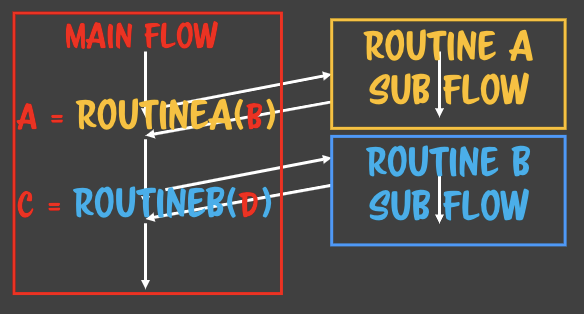
- 서브루틴을 부를 때부터 어느 포인트로 반환되는지 지정하고 부른다.
const routineA = b => {
const result = b * 2;
console.log(result);
return result;
};
const routineB = d => {
const result = d * 3;
console.log(result);
return d;
};
const b = 10,
d = 30;
const a = routineA(b);
console.log(a);
const c = routineB(d);
console.log(c);- 루틴이 개입하게 되면 프로그램의 흐름을 일자로 읽을 수 없다.
- 루틴에 대한 개념이 flow의 통제를 다른 곳에 줬다 뺏는 거라는 사실
왜 함수라고 안하고 서브루틴 이라고 할까?
- 함수는 수학적인 개념에 가깝다.
- flow를 컨트롤할 때 어떤 일이 일어나는지 알고 싶은 것.
- 이 관점에서는 함수를 function이라고 하지 않고
routine이라고 부른다.
Arrow function
참고 : http://webframeworks.kr/tutorials/translate/arrow-function/
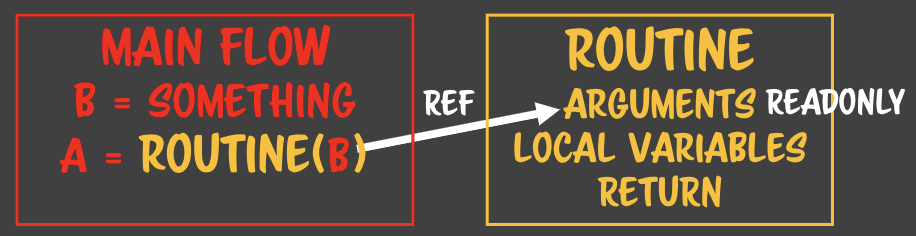
1-2. communicate with routine - main flow와 routine사이에 통신이라는 것을 한다. - 통신을 할 수
있는 매커니즘이 존재하는데, 이 매커니즘은 인자와 리턴이라고 알고 있다. - 자바스크립트에서는
return 없는 루틴은 없다.
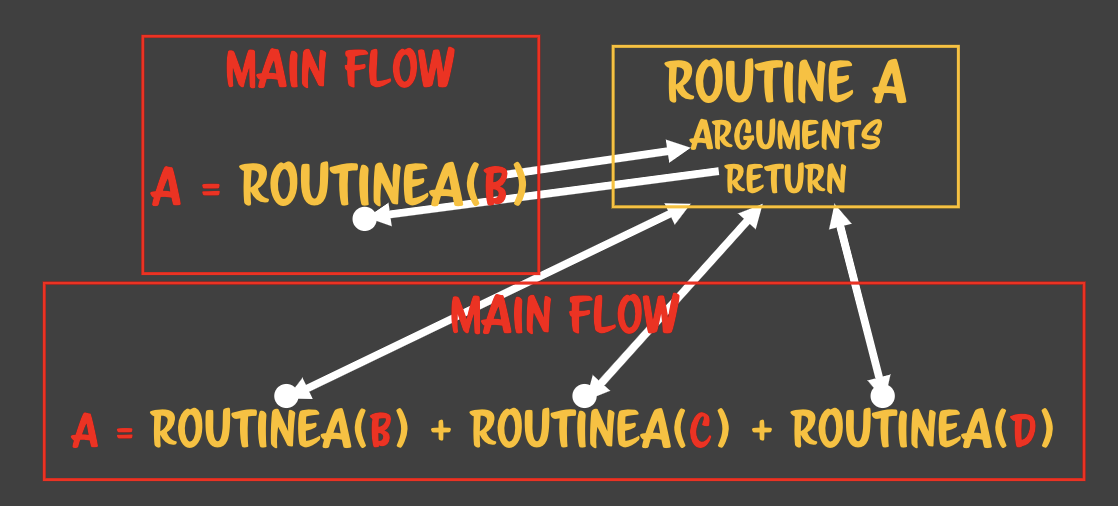
자바스크립트는 LR 파서를 사용한다. - 자바스크립트로 작성된 파일을 파싱할 때 사용하는 방법 -
왼쪽에서 오른쪽, 위에서 아래로 파싱 - 할당은 RL 파서이다. - 수학적인 컨텍스트로 정의되어있다.
const routineA = arg => {
const result = arg * 2;
return result;
};
const b = 10,
c = 20,
d = 30;
const a = routineA(b) + routineA(c) + routineA(d);덧셈 연산자에는 메모리가 필요하다.
- 갔다와서 들온 값을 기억하지 못하면 그다음 값이 들어올때까지 연산을 진행시킬 수 없다.
- 연산은 메모리를 만들어내고, 메모리가 연산이 해소될때까지 해제되지 않는다.
- 더하기 제거와 연산자 제거가 꼬리물기 최적화의 핵심이 된다.
- 연산이 꼬리물기 최적화에 방해를 된다.
- 연산이 계속 스택 메모리를 생산해 낸다.
1-3. sub routine in sub routine
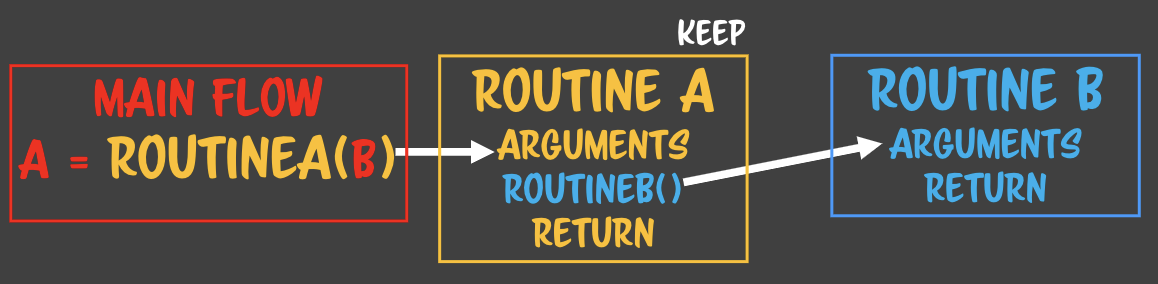 - 루틴A에서 루틴B가 호출될때 루틴A에서는
keep이 이루어진다. 메모리를 기억하는 행위. 스냅샷으로 기억해둔다. -
루틴B가 진행되고 루틴A로 반환되면 keep은 사라진다.
- 루틴A에서 루틴B가 호출될때 루틴A에서는
keep이 이루어진다. 메모리를 기억하는 행위. 스냅샷으로 기억해둔다. -
루틴B가 진행되고 루틴A로 반환되면 keep은 사라진다.
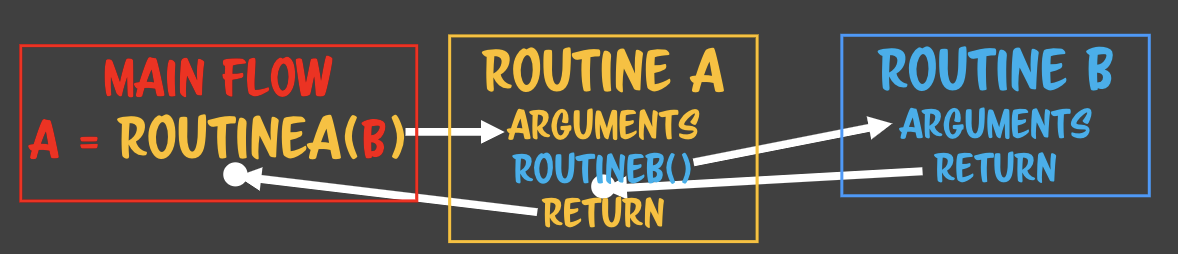
코드로 표현하면
const routineA = arg => routineB(arg * 2);
const routineB = arg => arg * 3;
const b = 10;
const a = routineA(b);스택메모리, 콜스택
극단적인 예
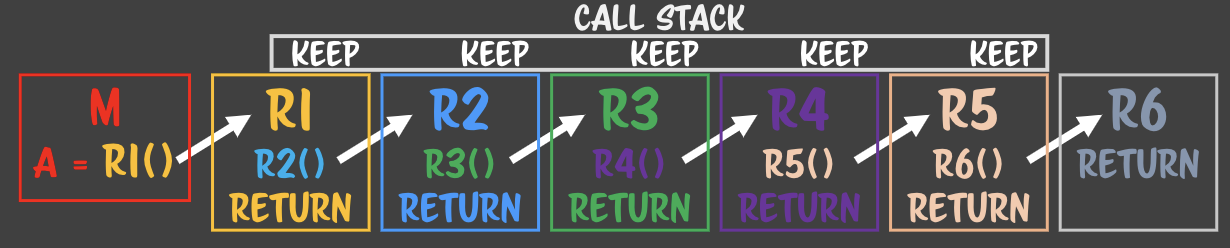 - R6에 도달하기위해 5개의 메모리를 기억해야한다. -
콜스택, 함수의 스택메모리라고 부른다. - 자바에서는 메모리를 1000개까지 잡을 수 있도록 도와주고,
자바스크립트에서는 100번만 하라고.. - 브라우저마다 콜스택 지원이 다르다. - 스택이 너무 넘처서 죽는
상황 : stackoverflow
- R6에 도달하기위해 5개의 메모리를 기억해야한다. -
콜스택, 함수의 스택메모리라고 부른다. - 자바에서는 메모리를 1000개까지 잡을 수 있도록 도와주고,
자바스크립트에서는 100번만 하라고.. - 브라우저마다 콜스택 지원이 다르다. - 스택이 너무 넘처서 죽는
상황 : stackoverflow
코드로 표현하면
const r1 = a => r2(a * 2);
const r2 = a => r3(a * 2);
const r3 = a => r4(a * 2);
const r4 = a => r5(a * 2);
const r5 = a => r6(a * 2);
const r6 = a => a * 5;
const b = 10;
const a = r1(b);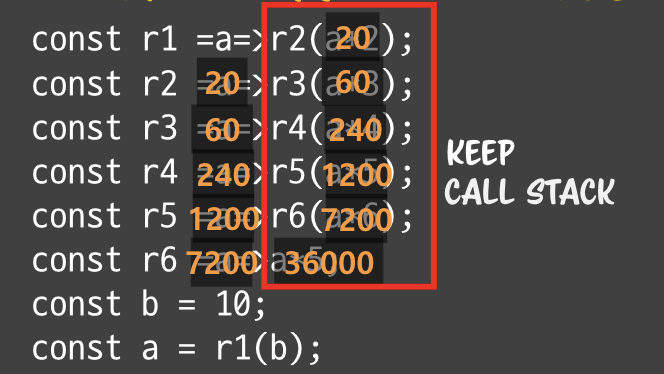
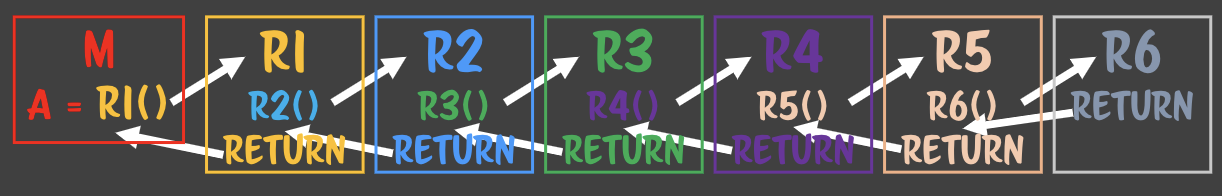
서브루틴 안에 서브루틴이 들어가면 기본적으로 이런 일이 일어난다.
1-4. Value vs Reference 값과 참조 값은 메모리상에서 전달할 때마다 복사되는 형태, 참조는
메모리상에서 공유된 객체의 포인터만 전달되는 형식
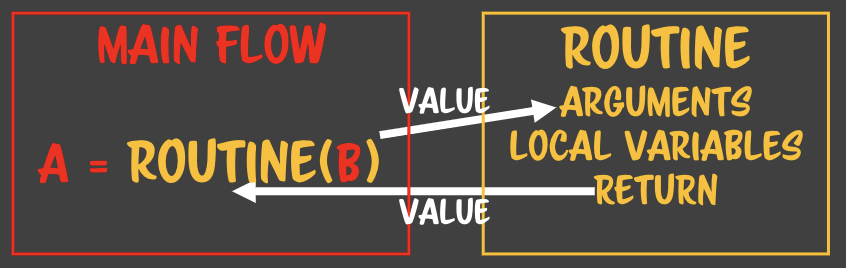
POINT- 값이 넘어가면 복사된 값이 넘어가기 때문에 해당 루틴에서 값이 변화가 일어나도 main flow에서는 값에 영향을 주지 않는다. - 루틴에서 return 되는 값도 복사본이 넘어가기 때문에 main flow는 새로운 복사본을 받게 되는 개념이다. - 즉, main flow와 루틴 사이에는 의존성이 낮아진다. - 값의 정의는 언어마다 다르다. - 문자열은 자바스크립트에서 값이지만 자바에서는 참조로 정의되고 있다. - 자바스크립트는 6개(es6 기준: number, string, boolean, undefined, null, symbol)

- 하나의 루틴이 여러 flow를 상대하고 있어도 아무 문제가 생기지 않는다.
- 복사본만 주고받기 때문에
상태안정이라고 부른다. State safe
- 수학적 프로그래밍의 기반이 된다.
- 값을 컨택스트로 해서 함수형 프로그래밍을 하려고 한다.
- 어디에서 누가 몇번을 부르던 상관없다.
- 완전 수학적 함수라고 한다.
- 때문에 처음 함수를 작성할 때 인자를 값으로 넘기는지부터 확인해보면 안전한 함수를 짤 수 있다.
const routine = a => a * 2;
const flow1 = _ => {
const b = 10,
d = 20;
const a = routine(b);
const c = routine(c);
return a + c;
};
const flow2 = _ => {
const b = 30,
d = 40;
const a = routine(b);
const c = routine(c);
return a + c;
};
flow1();
flow2();상황1: 참조로 넘겼을 때 참조값을 바꾸는 상황

const routine = ref =>
['a', 'b'].reduce((p, c) => {
// p는 콜백의 반환값, 초기값이 있을 경우 그값, 또는 콜백의 마지막 호출에서 이전에 반환된 누적값,
// c는 배열 내 현재 처리되고 있는 요소.
delete p[c];
return p;
}, ref);
const ref = { a: 3, b: 4, c: 5, d: 6 };
const a = routine(ref);
ref === a; // true
// 하나의 객체를 참조하고 있으므로.- 잘 통제할 수 없으면 복잡해지는 로직이다.
상황2: 참조로 넘겼을 때 참조값을 readOnly로만
const routine = ({a, b, ...rest}) => rest;
// spread 문법
// 새로운 객체가 반환된다.
const ref = {a:3, b:4, c:5, d:6};
const a = routine(ref);
ref !== a // truespread 문법 (참고: https://developer.mozilla.org/ko/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Operators/Spread_syntax )
-
웬만하면 reference를 인자로 넘기지 말고, 넘길수 밖에 없다면 readonly로 사용해라!!
- 그래야 함수의 side effect 효과를 줄일 수 있다.
상황3: 지역변수에 객체가 있거나, 리턴값이 객체인 경우
const routine = ref => {
const local = ref; // 지역변수에 참조본을 담았다.
local.e = 7; // ref 객체의 e에 7이 할당됨, 변화됨..
return local;
};
const ref = { a: 3, b: 4, c: 5, d: 6 };
const a = routine(ref);
ref === a; // true- 로컬이나 리턴할때도 새로운 객체를 만들어서 반환해주자!!!
const routine = ref => ({ ...ref, e: 7 });
const ref = { a: 3, b: 4, d: 5, d: 6 };
const a = routine(ref);
ref !== a; // truespread연산자는 순서에 영향이 있다. 이전에는 hash map이였는데, linked hash map이됨. 객체를 넣는 순서가 보장이 된다.
2. Structured design ## 높은 응집도, 낮은 결합도 High Cohesion, Loose Coupling
Larry constantine_ Structured design - 어떤 함수 내부의 코드가 높은 응집도를 갖는다? - 하나의 함수로 여러가지 처리를 할 수 있다. - 결합도가 높다? - 의존성이 높다.
좋은 서브루틴이란 높은 응집도와 낮은 결합도를 갖도록 짜야한다!
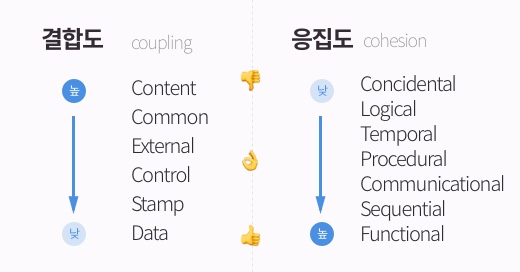
2-1. 결합도 coupling 👎👌👍
Content (👎 초강결합)
A클래스 속성v가 변경되면 즉시 B클래스가 깨짐
const A = class {
constructor(v) {
this.v = v;
}
};
const B = class {
constructor(a) {
this.v = a.v;
}
};
const b = new B(new A(3));- A와 B는 content coupling하고 있다.
Common (👎 초강결합)
Common클래스 변경 시 즉시 A,B클래스가 깨짐
- Common은 전역객체 혹은 공유객체
const Common = class {
constructor(v) {
this.v = v;
}
};
const A = class {
constructor(c) {
this.v = c.v;
}
};
const B = class {
constructor(c) {
this.v = c.v;
}
};
const a = new A(new Common(3));
const b = new B(new Common(5));External (👎 초강결합)
A, B 클래스는 외부의 정의에 의존함. member의 json 구조가 변경되면 깨짐.
- 나쁘지만 회피할 방법이 없다.
- 주로 외부에서 주어지는 객체
const A = class {
constructor(member) {
this.v = member.name;
}
};
const B = class {
constructor(member) {
this.v = member.age;
}
};
fetch('/memger')
.then(res => res.json())
.then(member => {
const a = new A(member);
const b = new B(member);
});- A와 B 클래스는 member json 스팩에 의존해있다.
- 때문에 api 문서들이 존재한다.
- 방법은 관리를 잘해야한다…
- 분기를 잘 태워주는 방법..
Control (👎 초강결합)
A클래스 내부의 변화는 B 클래스의 오작동을 유발
- 회피할 수 있는 방법이 생겼다.
- 루틴에게 직접적인 대상을 주지 않고 힌트를 주는 현상.
- class A가 변경될 경우 B가 깨진다.
- control 변수들 때문에..(case의 값들)
- 팩토리 패턴이 이런 이슈가 자주 일어난다.
- 전략패턴으로 바꾸면 해결 가능
const A = class {
process(flag, v) {
switch (flag) {
case 1:
return this.run1(v);
case 2:
return this.run2(v);
case 3:
return this.run3(v);
}
}
};
const B = class {
constructor(a) {
this.a = a;
}
noop() {
this.a.process(1);
}
echo(data) {
this.a.process(2, data);
}
};
const b = new B(new A());
b.noop();
b.echo('test');Stamp (👎👌 유사약결합)
- A와 B는 ref로 통신함.
- ref에 의한 모든 문제가 발생할 수 있음.
const A = class {
add(data) {
data.count++;
}
// data 전체를 받을 필요가 없고 count만 받았어야 한다.
// 넓은 범위로 받게 됨.
// count라는 변수명이 바뀌면 다 바뀌어야한다.
};
const B = class {
constructor(counter) {
this.counter = counter;
this.data = { a: 1, count: 0 };
}
count() {
// 필요한 값만 내려주자.
this.counter.add(this.data);
}
};
const b = new B(new A());
b.count();
b.count();Data (👌 약결합)
- A와 B는 value로 통신함 (값)
- 모든 결합문제에서는 자유로워짐
- data coupling만 생김.
- reference로 대화하게 되면 coupling이 높아진다.
const A = class {
add(count) {
return count + 1;
}
};
const B = class {
constructor(counter) {
this.counter = counter;
this.data = { a: 1, count: 0 };
}
count() {
this.data.count = this.counter.add(this.data.count);
}
};
const b = new B(new A());
b.count();
b.count();2-2. 응집도 cohesion 👎👌👍 ### Coincidental 우연히 👎 - 우연히 모여 있는.. - 아무런 관계가 없음.
- 다양한 이유로 수정됨 - 있는줄 모르고 또 만들게 된다.
const Util = class {
static isConnect() {}
static log() {}
static isLogin() {}
};Logical 👌
- 사람이 인지할 수 있는 논리적 집합.
- 언제나 일부만 사용됨.
- 주관적인 묶음..
- 도메인이 더 일반적이거나, 특수할 경우만!!
const Math = class {
static sin(r) {}
static cos(r) {}
static random() {}
static sqrt(v) {}
};Temporal 시간의 순서 👌
- 시점을 기준으로 관계없는 로직을 묶음.
- 관계가 아니라 코드의 순서가 실행을 결정.
- 역할에 맞는 함수에게 위임해야 함.
const App = class {
init() {
this.db.init();
this.net.init();
this.asset.init();
this.ui.start();
}
};Procedural 👌
- 절차적 순서
- 외부에 반복되는 흐름을 대체하는 경우.
- 순서 정책 변화에 대응불가.
const Account = class {
login() {
p = this.ptoken(); // permanet token
s = this.stoken(p); // session token
if (!s) this.newLogin();
else this.auth(s);
}
};Communicational 👌
- 하나의 구조에 대해 다양한 작업이 모여있음.
- 역할에 맞게 묶음.
const Array = class {
push(v) {}
pop() {}
shift() {}
unshift(v) {}
};Sequential
- 실행순서가 밀접하게 관계되며 같은 자료를 공유하거나 출력결과가 연계됨
- chaining 되고 있는 함수 메서드.
- Procedural + Communicational 개념
const Account = class {
ptoken() {
return this.pk || (this.pk = IO.cookie.get('ptoken'));
}
stoken() {
if (this.sk) return this.sk;
if (this.pk) {
const sk = Net.getSessionFromPtoken(this.pk);
sk.then(v => this.sk);
}
}
auth() {
if (this.isLogin) return;
Net.auth(this.sk).then(v => this.isLogin);
}
};Functional 👍
- 역할모델에 충실하게 단일한 기능이 의존성 없이 생성된 경우
- 앞으로 수업시간에 배워야할 부분
결합도와 응집도의 조화
높은 응집성을 갖게 되면 높은 커플링은 갖게된다. 결합도와 응집도의 조화를 목표로 로직을 짜야한다.